

What Is Severe Primary IGF-1 Deficiency?
- Height SDS* is ≤ -3.0
- IGF-1 concentration SDS ≤ -3.0
- Growth hormone is normal or elevated
Please see Indication and Important Safety Information below.
On this page

Olive, a former INCRELEX patient, at age 18, and her mother, Renee
IGF-1 Is Vital for Growth
Diagnosing and Testing
- History and examination
- Growth assessment
- Height velocity
- IGF-1 blood test
- GH stimulation test
- Bone age study
- Specialist imaging
History and Examination
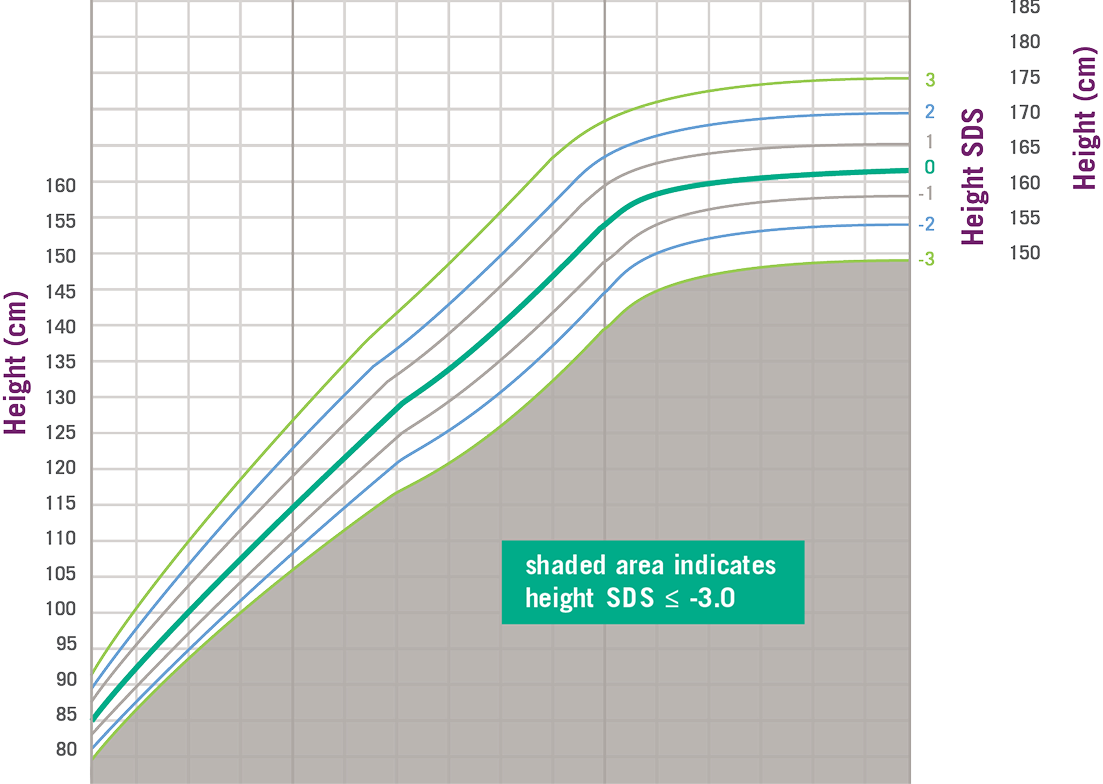
Growth Charts Can Help Diagnose Severe Primary IGF-1 Deficiency
*SDS, standard deviation score. Data and formula from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Growth Assessment
An example of a growth chart can be seen below. In this example, the expected average height is shown as a solid dark green line. Heights above and below this average are given a number to show how much they vary from the average height. This difference is called standard deviation.
In addition to measuring your child’s height, parents’ height may also be recorded.
This measurement is used to help doctors calculate what a child’s expected height could be. While it’s helpful to regularly measure your child’s height at home, having measurements taken at the doctor’s office may provide more consistent results.
Height Velocity
The speed at which your child is growing is known as the height velocity. This can be calculated by measuring your child’s height at regular intervals over a fixed time frame. Knowing a child’s height velocity can help a doctor determine if your child is growing at an expected rate.
IGF-1 Blood Test
If your doctor suspects your child has a growth disorder, a blood sample is likely to be taken and sent to a laboratory to measure levels of important hormones that influence growth, such as growth hormone and IGF-1.
If initial results show that there are low levels of growth hormone your doctor may suggest beginning treatment to increase the levels of this hormone. If your child is still not growing as expected, your doctor may also measure levels of IGF-1 in the blood to see if they may need to be supplemented. If IGF-1 treatment is considered, then IGF-1 levels may need to be measured periodically.
GH Stimulation Test
If tests show that IGF-1 levels are indeed low, a Growth Hormone (GH) stimulation test may be performed next, to see if your child has Severe Primary IGF-1 Deficiency.
A GH stimulation test will take place in the doctor’s office and your child will be given a medicine (usually by injection) that will stimulate their body to produce GH. Blood samples will be taken at regular intervals during this test. The samples will be sent to a laboratory for analysis and the results will let the doctor know how much GH your child released during the course of the test. Their results can then be compared to what would be expected for other children their age.
Severe Primary IGF-1 Deficiency occurs when GH levels in the blood are normal or even higher than might be expected and IGF-1 levels are very low (≤ -3.0 SDS), and their height falls more than three standard deviations below the average height for their age (i.e., ≤ -3 SDS).
Your child’s doctor will let you know what levels of IGF-1 and GH are considered normal.
Bone Age Study
A bone age study is a way for doctors to assess how a child’s skeletal system is maturing in comparison to the expected development for their age and gender. It traditionally involves taking a single X-ray of the left wrist and hand and comparing the images obtained to a standard set of images.
Children who have familial short stature or idiopathic short stature often have a bone age equivalent to their chronologic age. By contrast, those with a delay in growth due to puberty or hormonal disorders often have a bone age that is lower than their chronological age.
Specialized Imaging
Advocating for Your Child
You can help by being proactive and engaged in your child’s treatment. Ask your child’s doctor or nurse for information about your child’s condition and find out where you can learn more about the latest developments in diagnosis and treatment.
See the Support and Resources section of this website for educational materials and links to information on Severe Primary IGF-1 Deficiency.
Indication and important safety information
Important safety information
Always give Increlex exactly as your doctor directed.
Do not take INCRELEX if you are allergic to IGF-1 or any of its other ingredients. Report any allergic reactions.
INCRELEX should be injected under the skin and into the muscle. It should not be injected directly into a blood vessel.
INCRELEX should not be used after growth plates close which happens during puberty.
INCRELEX should not be used in children with cancerous tumors or a history of cancer.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): INCRELEX should be administered 20 minutes before or after a meal or snack and should not be administered when the meal or snack is skipped. Checking blood glucose levels is recommended. The dose of INCRELEX may need to be adjusted until an appropriate dose is decided by your doctor.
- Intracranial Hypertension: Increased pressure in your skull may occur because of cerebrospinal fluid buildup around your brain. Therefore, your doctor may require an eye examination at the start of Increlex treatment and periodically during the time you are taking INCRELEX.
- Lymphoid Tissue Hypertrophy: Lymphoid tissue hypertrophy is a noncancerous increase in the number of immune cells called lymphocytes. Patients should have periodic examinations with your doctor to rule out potential complications.
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a bone problem where the top of the upper leg (femur) slips apart. This may lead to a serious condition where bone tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply (osteonecrosis). Get medical help for your child right away if your child develops a limp or has hip or knee pain.
- Progression of Scoliosis: Your doctor will monitor you during treatment with INCRELEX if you have a history of scoliosis.
- Malignant Neoplasia: There have been reports of cancerous tumors in children who received INCRELEX. It is unknown whether there is any relationship between INCRELEX therapy and new occurrence of tumors. Tumors were mostly reported in patients with rare genetic conditions of short stature associated with a higher risk of cancer, or in patients already at risk of cancer. The tumors were seen more frequently in patients who received INCRELEX at higher than recommended doses or at doses that produced IGF-1 levels above normal for age and sex. Your doctor will carefully monitor you during your treatment with INCRELEX for development of tumors. If cancerous tumors develop, your doctor will stop your INCRELEX treatment.
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Infants due to Benzyl Alcohol Preserved Solution: Serious and fatal adverse reactions can occur in neonates and infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs. Use of INCRELEX in infants is not recommended.
The most common adverse reactions include low blood sugar, reactions at the injection site or throughout your body, and enlarged tonsils.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs by contacting Eton Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-855-224-0233 or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at www.fda.gov/safety/Medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see full Prescribing Information for more information.
Indication and important safety information
Important safety information
Always give Increlex exactly as your doctor directed.
Do not take INCRELEX if you are allergic to IGF-1 or any of its other ingredients. Report any allergic reactions.
INCRELEX should be injected under the skin and into the muscle. It should not be injected directly into a blood vessel.
INCRELEX should not be used after growth plates close which happens during puberty.
INCRELEX should not be used in children with cancerous tumors or a history of cancer.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): INCRELEX should be administered 20 minutes before or after a meal or snack and should not be administered when the meal or snack is skipped. Checking blood glucose levels is recommended. The dose of INCRELEX may need to be adjusted until an appropriate dose is decided by your doctor.
- Intracranial Hypertension: Increased pressure in your skull may occur because of cerebrospinal fluid buildup around your brain. Therefore, your doctor may require an eye examination at the start of Increlex treatment and periodically during the time you are taking INCRELEX.
- Lymphoid Tissue Hypertrophy: Lymphoid tissue hypertrophy is a noncancerous increase in the number of immune cells called lymphocytes. Patients should have periodic examinations with your doctor to rule out potential complications.
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a bone problem where the top of the upper leg (femur) slips apart. This may lead to a serious condition where bone tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply (osteonecrosis). Get medical help for your child right away if your child develops a limp or has hip or knee pain.
- Progression of Scoliosis: Your doctor will monitor you during treatment with INCRELEX if you have a history of scoliosis.
- Malignant Neoplasia: There have been reports of cancerous tumors in children who received INCRELEX. It is unknown whether there is any relationship between INCRELEX therapy and new occurrence of tumors. Tumors were mostly reported in patients with rare genetic conditions of short stature associated with a higher risk of cancer, or in patients already at risk of cancer. The tumors were seen more frequently in patients who received INCRELEX at higher than recommended doses or at doses that produced IGF-1 levels above normal for age and sex. Your doctor will carefully monitor you during your treatment with INCRELEX for development of tumors. If cancerous tumors develop, your doctor will stop your INCRELEX treatment.
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Infants due to Benzyl Alcohol Preserved Solution: Serious and fatal adverse reactions can occur in neonates and infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs. Use of INCRELEX in infants is not recommended.
The most common adverse reactions include low blood sugar, reactions at the injection site or throughout your body, and enlarged tonsils.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs by contacting Eton Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-855-224-0233 or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at www.fda.gov/safety/Medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see full Prescribing Information for more information.
